General information
Globin chain involved
Status
Double Heterozygous
Migration zones
Migration positions
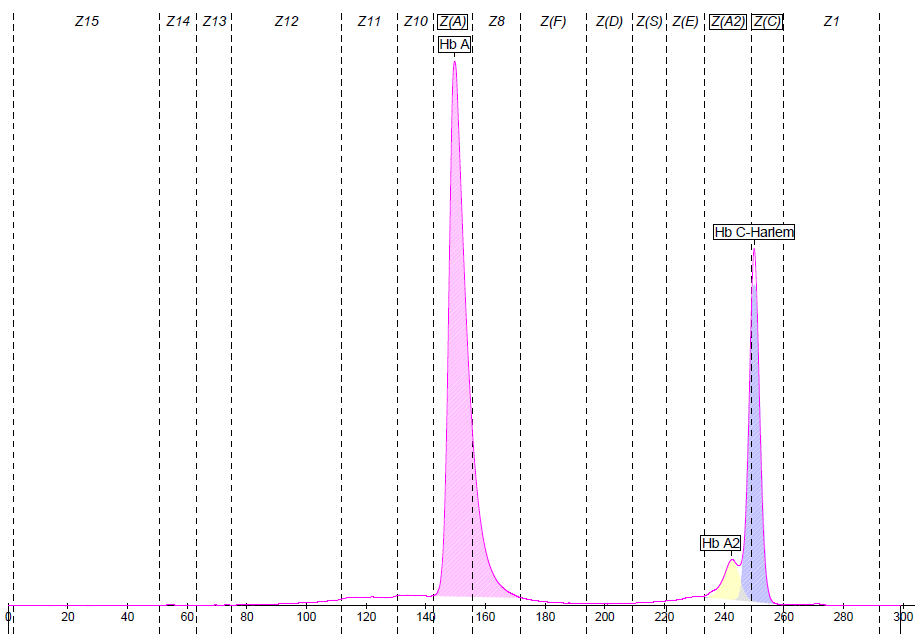
251
Sickle Cell Disease: Yes
Thalassemic variant: No
Capillary Electrophoresis
Fractions
Value %
Hb A
69.4
Hb A2
4.4
Hb C-Harlem
26.2
Comments
A 26.2% expression of Hb C-Harlem is consistent with a combination of this variant with an Alpha+-thalassemia (confirmed by genotyping). The high percentage of Hb A2 has not been elucidated.
Mutation data
Double Heterozygous Hb C-Harlem
Mutation
HGVS Nomenclature
Beta 6(A3) Glu>Val and Beta 73(E17) Asp>Asn
HBB:c.[20A>T;220G>A]
Alpha+-thalassemia
Mutation
HGVS Nomenclature
One of the many described Alpha gene defects reported on http://globin.cse.psu.edu/hbvar/menu.html
No information
Hematological parameters
Name
Result
RBC Count
No information
Total Hemoglobin
No information
MCV
Low
MCH
No information
Blood smear
No information
Other analysis
No information
Comments on hematology
Microcytosis due to Alpha-thalassemia
Clinical context
Clinical presentation
Normal
Clinical risk
This rare variant causes Sickle Cell Disease in association with Hb S. This variant is classified as a non-Hb S Sickling variant
Variant information
Stability
Unstable
Oxygen affinity
Normal
Ethnicities in literature
Found in Black African populations: met in several Black families in the USA
Comments on variant information
The rare variant Hb C-Harlem results from a double mutation of the beta chain (combination of Hb S and Hb G-Accra also called Hb Korle-Bu mutations, on the same beta gene).
Scientific Literature
Scientific references
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6016610/ Bookchin RM. et al., J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):248-55.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/5069596/ Lang A. et al., Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 31;278(1):57-61.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1148394/ Moo-Penn W. et al., Blood. 1975 Sep;46(3):363-7.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3611079/ Adachi K. et al., J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10470-4.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12693943/ Adachi K. et al., Biochemistry. 2003 Apr 22;42(15):4476-84.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29365076/ Riou J. et al., Am J Clin Pathol. 2018 Jan 29;149(2):172-180.
Globin Chain involved
Status
The term "Double Heterozygous" refers to cases of heterozygosity on different globin chain types, while the term "Compound Heterozygous" refers to cases of heterozygosity on the same globin chain type.
For example, S/G-Pest is a Double Heterozygous case (beta and alpha-globin chains are mutated) and S/C is a Compound Heterozygous case (only beta-globin chains are mutated).
Migration zones
Migration positions
In some cases (homozygotes, combination of the variant with thalassemia, transfused patients, degraded samples or unstable variants), the variation in the migration position may be greater than +/- 1 point.
For profiles with thalassemia, only Hb A2 and Hb F peaks, if present, are listed with migration positions.
Sickle Cell Disease
Thalassemic variant
Capillary Electrophoresis
Variant information
Ethnicities are provided for informational purposes only and are based on scientific literature and conference posters.
A hemoglobin variant may therefore be present in populations of ethnic origins or countries not listed here.
Hematological Parameters